
Introduction: Volleyball is a dynamic and fast-paced sport that requires teamwork, strategy, and a clear understanding of each player’s role on the court. For beginners, grasping the different positions and their responsibilities is crucial for effective gameplay and overall team success. In volleyball, there are typically six positions on the court, each with specific functions that contribute to the team’s performance. Understanding these roles will not only help you find your place on the team but also enhance your appreciation of the game.
| Outside Hitter | Katarina Johnson-Thompson, Matt Anderson |
| Setter | Micah Christenson, Kim Yeon-koung |
| Libero | Fabian Ruiz, Saeid Marouf |
| Opposite Hitter | Wilfredo León, Kamil Semeniuk |
| Middle Blocker | Antonov Ivanov, Matija Zaitsev |
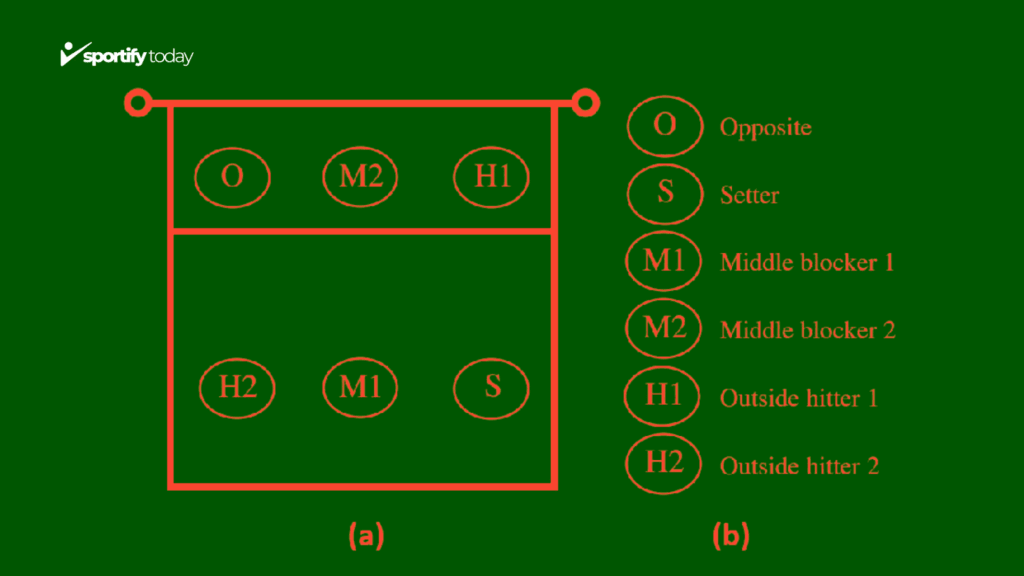
Volleyball Court Positions Explained

Understanding the various positions on the volleyball court is essential for players and coaches alike. Each position has specific responsibilities that contribute to the overall success of the team. Here’s a breakdown of the key volleyball positions
1. The Role of the Setter in Volleyball
The setter is often referred to as the playmaker of the team. Their primary responsibility is to deliver accurate sets to the hitters, creating scoring opportunities. A good setter must possess excellent decision-making skills, quick reflexes, and the ability to read the game effectively.
| Setting | The primary role of the setter is to deliver accurate sets to hitters, positioning the ball for an effective attack. |
| Decision-Making | Setters must quickly decide which teammate to pass the ball to, often under pressure, to maximize scoring chances. |
| Ball Control | Precise ball control is crucial for the setter, as they touch the ball more than any other player during a game. |
| Communication | Setters must constantly communicate with teammates to coordinate plays and signal their intended sets. |
| Defense | Aside from setting, setters also play a critical role in defense, covering tips and reacting to fast-paced play. |
Duties: The setter is responsible for delivering accurate sets to the hitters, determining the tempo of the offense, and making quick decisions based on the game situation.
Responsibilities: They must read the defense, communicate with teammates, and often play a crucial role in both offense and defense by covering tips and blocks.
2. The Role of the Outside Hitter in Volleyball
The outside hitter, also known as the left-side hitter, is typically the primary attacker. They play a crucial role in both offense and defense, hitting from the left side of the court and receiving serves. Outside hitters need strong all-around skills, including attacking, passing, and digging.
| Attacking | The primary role is to attack from the left side of the court, aiming for kills to score points. |
| Serve Reception | Outside hitters are often responsible for receiving serves, helping the team transition into offense. |
| Blocking | They block opponents’ attacks, especially on the right side of the net, to defend their team. |
| Defense | In the back row, they play a key role in defending against opposing spikes and covering tips. |
| Versatility | Outside hitters need to be well-rounded, participating in both offense and defense throughout the game. |
Duties: The outside hitter attacks the ball from the left side of the court, receives serves, and plays defense.
Responsibilities: They are expected to score points through powerful attacks, pass effectively, and dig defensive plays. They also participate in blocking at the net.
3. The Role of the Middle Blocker in Volleyball
Positioned at the net, the middle blocker focuses on blocking the opposing team’s attacks and executing quick offensive plays. They need to have good timing and positioning to effectively block and also contribute to the team’s offense with quick sets.
| Blocking | The primary role of the middle blocker is to block opposing hitters, especially those at the net, to stop or deflect attacks. |
| Quick Attacks | Middle blockers execute fast, often low sets, leading to quick offensive plays and surprise attacks. |
| Anticipation | They must read the setter and anticipate the opponent’s moves to position themselves for effective blocks. |
| Defense | Middle blockers also help in back-row defense, especially covering tips and soft attacks from the opposition. |
| Communication | They need to communicate effectively with the setter and teammates to organize blocks and transitions to offense. |
Duties: Positioned at the net, the middle blocker focuses on blocking the opposing team’s attacks and executing quick offensive plays.
Responsibilities: They must time their jumps to block attacks, set up quick sets for attacks, and provide support in defense by covering tips and off-speed shots
4. The Role of the Opposite Hitter in Volleyball
The opposite hitter plays opposite the setter and is responsible for attacking from the right side of the court. They often have a dual role in both offense and defense, blocking the opposing outside hitter and providing additional scoring options for the team.
| Attacking | Primary attacker from the right side, focusing on powerful hits. |
| Blocking | Blocks against the opponent’s outside hitters, strong at the net. |
| Versatility | Contributes both offensively and defensively, versatile in play. |
| Back Row Attacks | Can attack from the back row, adding to offensive threats. |
| Support the Setter | Provides support to the setter during plays and ball transitions. |
Duties: The opposite hitter plays opposite the setter and attacks from the right side of the court, often serving as a secondary attacker.
Responsibilities: They contribute to both offense and defense, blocking the opposing outside hitter and providing scoring options through attacks and tips.
5. Serving Specialist
The serving specialist is a player who is brought in specifically to serve. They typically possess a strong serve and may be substituted in for a front-row player. Their role is to create scoring opportunities through effective serving.
| Role | Focuses on delivering powerful and accurate serves to put pressure on the opponent. |
| Key Skill | Mastery of various serving techniques, such as jump serves and float serves. |
| Game Impact | Can change the momentum of the game with well-executed serves. |
| Playing Time | Typically brought in for specific serving situations. |
Duties: The serving specialist is brought in specifically to serve, typically possessing a strong serve that can create scoring opportunities.
Responsibilities: They focus on delivering effective serves, often aiming for aces or challenging the opponent’s serve reception.
6. Understanding the Libero Position in Volleyball
The libero is a specialized defensive player who wears a different color jersey. Their primary focus is on receiving serves and playing defense. Liberos cannot attack the ball above the net and are not allowed to serve or block. They are essential for improving the team’s defensive capabilities.
| Role | Specialized defensive player, primarily responsible for receiving serves and digging attacks. |
| Restrictions | Cannot attack above the net or serve; often wears a different color jersey. |
| Key Skills | Excellent passing, digging, and defensive skills, with quick reflexes and agility. |
| Substitution | Can replace any back-row player without a limit on substitutions. |
Duties: The libero is a defensive specialist who wears a different color jersey and focuses on receiving serves and playing defense.
Responsibilities: They cannot attack the ball above the net and are responsible for digging, passing, and improving the team’s overall defense without serving or blocking.
7. Defensive Specialist
Similar to the libero, the defensive specialist focuses on defense and serve reception. However, unlike the libero, they can play in the front row and participate in attacking plays. They are often substituted in for a front-row player to enhance the team’s defense.
| Role | Focused on defensive plays, including receiving serves and digging attacks. |
| Key Skills | Excellent at receiving serves, digging, and reading opponent’s attack patterns. |
| Playing Time | Used in back-row positions and substituted for specific defensive situations. |
| Restrictions | Cannot attack the ball above the net; similar role to a Libero but with different substitution rules. |
Duties: Similar to the libero, the defensive specialist focuses on defense and serve reception but can play in the front row.
Responsibilities: They are often substituted in for a front-row player to enhance defensive capabilities and may participate in attacking plays when in the front row.
Tips for Beginners on Volleyball Positions and Roles
As a beginner in volleyball, understanding the different positions and their roles can seem daunting at first. However, with some guidance and practice, you can quickly grasp the basics and start contributing to your team’s success. Here are some tips to help you navigate the various volleyball positions and roles
| Outside Hitter | Focus on strong attacking and defensive skills; work on timing for effective spikes and blocks. |
| Setter | Improve ball-handling skills and communication; practice setting accurate and quick balls. |
| Libero | Specialize in receiving serves and digging; work on passing accuracy and defensive positioning. |
| Opposite Hitter | Develop versatility in attacking and blocking; practice powerful hits and effective defensive plays. |
| Middle Blocker | Focus on timing for blocking and quick lateral movements; improve vertical jump and net defense. |
1. Familiarize Yourself with the Court
Learn the dimensions of the volleyball court and the positions of the players on the court.
Understand the rotation order and how players move from one position to another during gameplay.
2. Identify Your Strengths and Weaknesses
Assess your physical attributes, such as height, jumping ability, and hand-eye coordination.
Determine your skill set and focus on developing your strengths while improving your weaknesses.
3. Practice Multiple Positions
During training, try playing different positions to gain a better understanding of each role and its responsibilities.
This will help you become a more versatile player and make you a valuable asset to your team.
4. Communicate with Your Teammates
Effective communication is crucial in volleyball, especially when playing specific positions.
Learn to communicate with your teammates, especially the setter, to ensure smooth gameplay and effective execution of plays.
5. Understand Rotational Patterns
Familiarize yourself with the rotational patterns in volleyball, where players move to different positions after each rally.
Knowing the rotational patterns will help you anticipate your next position and responsibilities on the court.
6. Focus on Developing Core Skills
Regardless of your position, focus on developing core skills such as passing, setting, hitting, and serving.
These skills are essential for all players and will help you contribute to the team’s success in any position.
7. Observe and Learn from Experienced Players
Watch and learn from experienced players in your position or other positions.
Pay attention to their techniques, decision-making, and positioning on the court.
8. Be Adaptable and Coachable
Be open to feedback and coaching suggestions regarding your position and role on the team.
Adaptability is key, as you may need to adjust your position or responsibilities based on the team’s needs or game situations.
How to improve Volleyball Positions in game play

| Anticipate the Play | Read the game and predict the opponent’s next move to position effectively. |
| Communicate with Teammates | Use clear cues for smooth teamwork and effective play execution. |
| Adjust Position Based on Rotation | Modify positioning according to team rotation and court alignment. |
| Maintain Proper Footwork | Ensure correct foot placement and stance for balance and agility. |
| Analyze Game Footage | Review games to identify strengths, weaknesses, and improvement areas. |
| Adapt to Game Situations | Adjust strategies based on game flow and opponent’s playing style. |
Conclusion: Understanding volleyball positions and their roles is essential for beginners to enhance teamwork and gameplay. By familiarizing themselves with each position’s responsibilities and focusing on core skills, players can contribute effectively to their team’s success.
People also ask
1.What are the key rules of volleyball?
The key rules of volleyball include allowing a maximum of three touches per team to return the ball over the net, with players rotating clockwise after gaining the serve. Teams score points by grounding the ball in the opponent’s court or forcing errors

Leave a Reply