
Introduction : Some of the richest sources of Vitamin B12 include shellfish, fish, and Animal food products. Here are the Top 14 Vitamin B12 Foods to improve good health .These foods are especially crucial for DNA synthesis and red blood cell production and support the immune system while maintaining healthy nerve functioning.
Though there are many B12-ribbed animal-based foods, it is equally important to remember that B12 fruits veggies generally do not contain naturally occurring amounts of this vitamin. Fortified plant-based alternatives include cereals and Animal food products that can be used to complement the deficiency to ensure that an adequate intake level of folate is achieved for vegetarian diets, as well as vegan diets.
Unless you are consuming the animal-based products, you should, most importantly, obtain the fruits and vegetables that are fortified with B12. For example, you could eat fortified mushrooms or a combination of natural and fortified food items.
Top 14 Best Sources b12 fruits vegetables
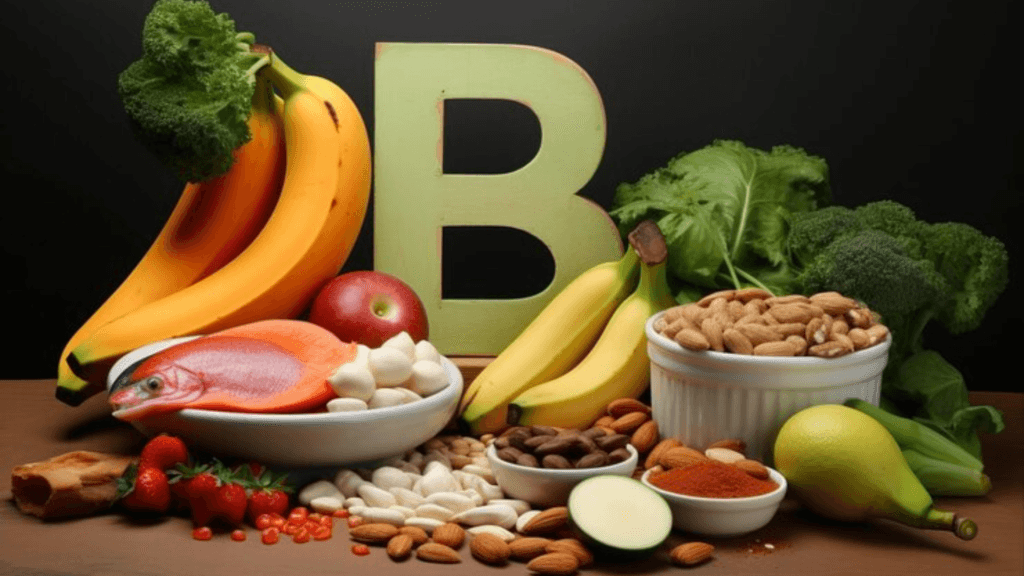

| Food | Energy Levels (kcal) | Vitamin B12 (mcg) | Vitamin C (mg) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Animal liver and kidneys | 130 | 70.7 | 0 |
| Clams | 148 | 98.9 | 0 |
| Sardines | 208 | 8.9 | 0 |
| Beef | 250 | 2.5 | 0 |
| Fortified cereal | 100 | 6.0 | 0 |
| Tuna | 132 | 2.5 | 0 |
| Fortified nutritional yeast | 60 | 24.0 | 0 |
| Trout | 191 | 5.4 | 0 |
| Salmon | 206 | 3.2 | 0 |
| Fortified nondairy milk | 40 | 1.2 | 0.5 |
| Cow’s milk and other dairy products | 60 | 0.9 | 0 |
| Eggs | 155 | 1.1 | 0 |
| Oysters | 116 | 16.0 | 0 |
| Nutritional Yeast | 60 | 24.0 | 0 |
1.Animal Liver and Kidneys : The organ meats like the liver and kidney contain Vitamin B12 in it, which is necessary for the production of red blood cells and maintenance in healthy conditions of the nervous system, and are also this very nutrient. These are also valuable protein sources as well as the meat contains about 20-25 grams per 100 g of muscle.
2.Clams : The different vitamins and minerals found in the diet affect the body close to the brain in different aspects. They contain, for example, about 14-20 grams of protein per serving that is responsible for muscle building and healthy body. Clams release about 84 micrograms of Vitamin B12 in every 100 grams which is a vital element for the round-the-clock function of the brain and the transformation of energy.
3.Sardines: With vitamin B12 being only part of what sardines bring to the body, 100 grams serve to fit into 8.9 micrograms and 25 grams of protein, aiding muscle and American health. Also, lots of omega-3 will help with a heart sometimes, helpful against inflammation.
4.Beef : Beef is a very good source of Vitamin B12, containing roughly 2.6 micrograms per 100 grams, vital in the raring of a healthy nerve function and red blood cells. It also consists of some 26 grams of protein per serving, making it a great post-workout option for muscle gain and repair.
5.Fortified Cereal : Fortified cereals also contain Vitamin B12: around 6 micrograms per serving, therefore they are an excellent alternative for vegans and vegetarians. Several vitamins and minerals are added to most fortified cereals; they can easily augment daily nutrient requirements, each serving providing about 3-5 grams of protein.
6.Tuna : Rich in vitamin B12, tuna affords around 2.5 micrograms of vitamin B12 per 85-gram service, facilitating the formation of blood cells and ensuring health for targeted nerves. In addition, tuna is full of proteins: nearly 22 grams of protein per serving, so it’s an excellent choice for muscle repair and rebuilding.
7.Fortified Nutritional Yeast : The fortified nutritional yeast is just one source of plant-based proven to contain Vitamin B12 that exceeds over 24 micrograms per serving of two tablespoons. This amount thus helps one to produce energy through metabolism, as well as giving proper functioning to the nervous system.
Its nearly 8 grams of protein per serving makes it an especially helpful source for muscle mass and overall nutrition for vegetarians and vegans.
8.Trout : Trout is the richest source of Vitamin B12, about 5.4micrograms per every 100g; it is responsible for red blood cell formation, and nerve health in general. Its serving has around 20g of protein, which makes it a worthy nutritional substitute for muscle repair and general well-being.
9.Salmon : Trout offers about 5.4 ug of Vitamin B12 per 100 grams, making trout an exhaustive source of this important Vitamin.
10.Fortified Nondairy Milk : Fortified nondairy milk products—such as soy or almond milk—were added with Vitamin B12. Up to 1.2 micrograms of that vitamin were found in one cup—needed in red blood cells and the nervous system.
It also holds 1-8 grams of proteins per serving depending on the type of milk, thus, it is an important contributing source for muscle maintenance along with health.
11.Cow’s Milk and Other Dairy Products : Close to 0.9 micrograms-cup, cow’s milk and other dairy products correspond to an excellent source of Vitamin B12. They have about 8 grams of proteins that are effective for muscle recovery and endurance. Besides, these foods supply calcium and important vitamins like D, which assist normal bone development.
12.Eggs : The richness of eggs comes from the high-quality protein content. An egg contains almost 6 grams of protein. Another nutrient containing eggs is Vitamin B12.
13.Oysters : Oysters are nutrient-rich foods they supply about 10 grams of protein per 3-ounce serving, and they also are rich in vitamin B12, which can facilitate nerve function and DNA synthesis. They further boast high amounts of zinc, which is helpful for the immune system and cellular repair, so this food is truly a powerhouse toward complete wellness.
14.Nutritional Yeast : Nutritional yeast is a source of complete protein, with approximately 8 grams of protein per serving of two tablespoons. It also contains many nutrients and especially much vitamin B12.
Therefore, it is an excellent choice for vegans and vegetarians, as the unique flavor adds to the beauty of the dish and contributes to nutritional content supporting energy production and overall health.
Key Benefits of Vitamin B12 for Humans

Vitamin B12 is involved in red blood cell formation, and its deficiency brings about anemia and less energy. For this reason, B12 enhances the well-being and normal functioning of the brain, hence upgrading the memory and moods of a person.
It also increases DNA synthesis besides maintaining the effective working of the nervous system. Finally, it also keeps one’s heart healthy by regulating homocysteine levels as well as preventing various cardiovascular diseases. This makes sure that anemia is eradicated, and therefore oxygen transport is proper throughout the body.
Supports Nerve Functioning: Vitamin B12 helps the body form DNA and keep nerves healthy to function properly. It also controls homocysteine, which in turn reduces the disease risk associated with heart conditions and ensures that your heart remains healthy. It is also necessary for nerve cells to function well.
Higher levels of energy- Though it acts very significantly on metabolism, especially on how the food
transformed into energy: deficiency causes fatigue and weakness.
Helps in DNA Synthesis-Vitamin B12 is needed in the synthesis of DNA and for supporting cellular replication and repair processes critical for all-round health.
Improvement in mood and cognitive function: The appropriate amount of B12 has a direct positive correlation to mood and clear thinking. Deficiency may be associated with mood disorders and decline in cognitive function.
Foods to improve vitamin b12 deficiency

Precautions to be taken: Limit processed foods and food items that are low on animal products in your diet as usually they do not contain sufficient levels of this vital nutrient. Instead, have whole foods like meat, fish, dairy, and fortified cereals for the highest B12 levels.
Dietary intakes that interfere with Vitamin B12 absorption can be avoided to prevent deficiency. In fact, here is a list of things that can be taken to a minimum and some things that can be entirely removed from diets
Foods to Limit in Order to Prevent Vitamin B12 Deficiency

High-Fiber Foods: Food containing dietary fiber, such as bran and some legumes, also lowers the amount of B12 that is absorbed.
Processed Foods: If they’re not fortified, most processed foods don’t contain nearly enough B12
Alcohol: If you drink too much you may not absorb vitamin B12 as well and you can end up harming your own liver so it can store this vitamin.
Some Medications: There are also diabetes drugs such as metformin and for acid reflux, proton pump inhibitors, which slows down the absorption of B12.
Raw fish and shellfish: Cooked forms are conveniently beneficial, but raw or partially raw fish and shellfish sometimes interfere with absorption of B12 if there is a special protein capable of binding the vitamin.
Non-dairy creamers: Most non-dairy creamers aren’t fortified with B12. A large number of people substitute these for milk; frequent use over time will lead to deficiencies.
Dry Fruits with Higher Concentrations of Vitamin B12

While dry fruits are a completely negligible source of vitamin B12, on the other hand, there are fortified variations. These are dried fruits that have been enriched in the vitamin, such as some brands of dried apricots and figs.
Raisins and dates are traditional dry fruits but they don’t contain any vitamin B12. Instead include more B12 rich food items i.e animal products or fortified ones.
| Dry Fruits | Description |
|---|---|
| Fortified Dried Apricots | Some brands add B12 to enhance their nutritional profile. |
| Fortified Figs | Look for options that specify added B12. |
| Raisins and Dates | Generally low in B12 but may be fortified. |
While dry fruits are typically not significant sources of vitamin B12, checking for fortified options can help enhance your intake. It’s essential to combine these with other B12-rich foods, such as animal products or fortified items.
Vitamin B12 vegetables and fruits
There is no naturally occurring Vitamin B12 content in any fruit or vegetable, but those can be found in fortified choices which help avoid deficiency. While none of the fruits and vegetables come close to the concentration of B12, there are plenty of plant foods that are created to include this essential nutrient. Fortified cereals, nutritional yeast and some non dairy milk choices all provide B12.
| Vitamin Source | Importance |
|---|---|
| Fortified Cereals | Enhances B12 intake for vegetarians and vegans. |
| Nutritional Yeast | Great source of B12, often fortified for better nutrition. |
| Fortified Plant-Based Milk | Provides B12 while catering to lactose intolerance. |
What Foods Can Help With Vitamin B12 Deficiency

Foods that could perhaps help bridge the deficiency of vitamin B12 are animal-based products like meat, fish, dairy, and eggs. Such foods are considered to be rich in this vitamin. In contrast, those under vegetarian and vegan diets can turn to other enriched products like breakfast cereals and plant-based milk.
Recommended Daily Amounts for Vitamin B12
| Age Group | Recommended Daily Amount of Vitamin B12 (mcg) | Calcium Percentage (% Daily Value) |
|---|---|---|
| Infants (0-6 months) | 0.4 mcg | 0% |
| Infants (7-12 months) | 0.5 mcg | 0% |
| Children (1-3 years) | 0.9 mcg | 0% |
| Children (4-8 years) | 1.2 mcg | 0% |
| Children (9-13 years) | 1.8 mcg | 0% |
| Teens (14-18 years) | 2.4 mcg | 0% |
| Adults (19-50 years) | 2.4 mcg | 30% |
| Adults (51+ years) | 2.4 mcg | 30% |
| Pregnant Women | 2.6 mcg | 30% |
| Lactating Women | 2.8 mcg | 30% |
Conclusion : Vitamin B12 is an essential nutrient for the human body, and hence performs many functions in it. In general, Vitamin B12 is found in animal foods like seafood, meat, milk, and fortified cereals. This vitamin B12 is available from nutritional yeast as well as some plant-based milks.
Frequency Asked Questions
1. What fruits and vegetables are high in B12?
Fruits and vegetables hardly contain any vitamin B12 at all, which is exclusively found in animal-based food products. Many plant milk and most breakfast cereals are, however, fortified with added B12. Nutritional yeast is also a great source for the vegan.
2. A carrots a good source of vitamin B12?
No Carrots are not good sources of vitamin B12. Carrots are very high in beta-carotene, which the body will convert to vitamin A but not B12. Vitamin B12 should come from an animal product, such as meat, fish, eggs, and dairy or fortified foods and supplements.

Leave a Reply